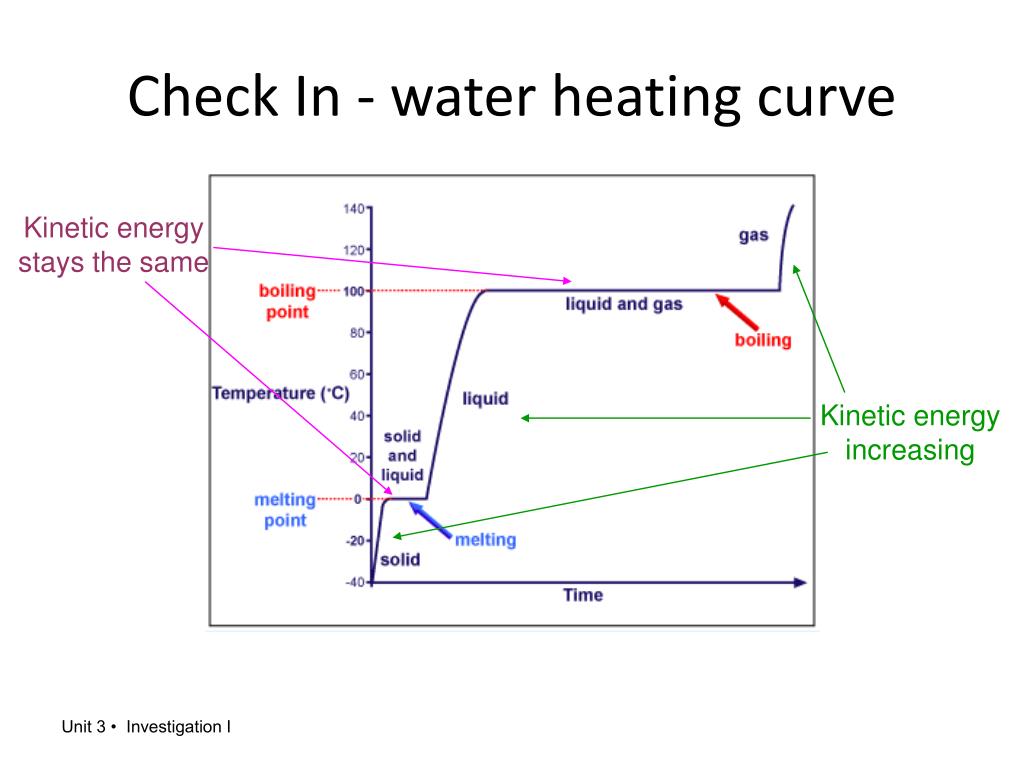
Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves . during the horizontal line segments, there is no change in temperature, so kinetic energy remains constant. the energy coming in results in higher potential energy not higher kinetic energy. heating and cooling curves are graphs. Since temperature is a measure of average kinetic energy, any. The ice is in a closed container. Breaking up the imf between the molecules leads to a high potential. continued heating of the water after the ice has completely melted will now increase the kinetic energy of the liquid molecules and the temperature will rise. for example, converting a liquid, in which the molecules are close together, to a gas, in which the molecules are, on average, far apart,. Imagine that you have a block of ice that is at a temperature of −30oc − 30 o c, well below its melting point. For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat. kinetic energy, potential energy and a heating curve.
from www.slideserve.com
Since temperature is a measure of average kinetic energy, any. Imagine that you have a block of ice that is at a temperature of −30oc − 30 o c, well below its melting point. for example, converting a liquid, in which the molecules are close together, to a gas, in which the molecules are, on average, far apart,. continued heating of the water after the ice has completely melted will now increase the kinetic energy of the liquid molecules and the temperature will rise. The ice is in a closed container. Breaking up the imf between the molecules leads to a high potential. kinetic energy, potential energy and a heating curve. during the horizontal line segments, there is no change in temperature, so kinetic energy remains constant. heating and cooling curves are graphs. the energy coming in results in higher potential energy not higher kinetic energy.
PPT Heating/Cooling Curves & Q= mC Δ T PowerPoint Presentation ID
Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves Breaking up the imf between the molecules leads to a high potential. the energy coming in results in higher potential energy not higher kinetic energy. for example, converting a liquid, in which the molecules are close together, to a gas, in which the molecules are, on average, far apart,. For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat. heating and cooling curves are graphs. Imagine that you have a block of ice that is at a temperature of −30oc − 30 o c, well below its melting point. during the horizontal line segments, there is no change in temperature, so kinetic energy remains constant. Since temperature is a measure of average kinetic energy, any. Breaking up the imf between the molecules leads to a high potential. continued heating of the water after the ice has completely melted will now increase the kinetic energy of the liquid molecules and the temperature will rise. The ice is in a closed container. kinetic energy, potential energy and a heating curve.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT A.P. Chemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1875178 Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves The ice is in a closed container. kinetic energy, potential energy and a heating curve. Breaking up the imf between the molecules leads to a high potential. continued heating of the water after the ice has completely melted will now increase the kinetic energy of the liquid molecules and the temperature will rise. the energy coming in. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From studylib.net
Heating and Cooling Curves Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves The ice is in a closed container. Since temperature is a measure of average kinetic energy, any. For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat. Imagine that you have a block of ice that is at a temperature of −30oc − 30 o c, well below its melting point. during the horizontal line segments, there is. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From www.ck12.org
Heating and Cooling Curves ( Read ) Chemistry CK12 Foundation Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves heating and cooling curves are graphs. continued heating of the water after the ice has completely melted will now increase the kinetic energy of the liquid molecules and the temperature will rise. during the horizontal line segments, there is no change in temperature, so kinetic energy remains constant. kinetic energy, potential energy and a heating curve.. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From www.youtube.com
2.5 Heating/Cooling Curves (Potential and Energy Changes) YouTube Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves Imagine that you have a block of ice that is at a temperature of −30oc − 30 o c, well below its melting point. The ice is in a closed container. the energy coming in results in higher potential energy not higher kinetic energy. heating and cooling curves are graphs. kinetic energy, potential energy and a heating. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From www.excelatphysics.com
Cooling Curve ExcelPhysics Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves kinetic energy, potential energy and a heating curve. the energy coming in results in higher potential energy not higher kinetic energy. during the horizontal line segments, there is no change in temperature, so kinetic energy remains constant. for example, converting a liquid, in which the molecules are close together, to a gas, in which the molecules. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From lessonschoolimbrowning.z14.web.core.windows.net
Heat And Cooling Curve Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves heating and cooling curves are graphs. The ice is in a closed container. during the horizontal line segments, there is no change in temperature, so kinetic energy remains constant. Breaking up the imf between the molecules leads to a high potential. kinetic energy, potential energy and a heating curve. For heating curves, we start with a solid. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From wisc.pb.unizin.org
M11Q2 Heating Curves and Phase Diagrams Chem 103/104 Resource Book Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves The ice is in a closed container. For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat. during the horizontal line segments, there is no change in temperature, so kinetic energy remains constant. continued heating of the water after the ice has completely melted will now increase the kinetic energy of the liquid molecules and the temperature. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From www.worldwisetutoring.com
Heating and Cooling Curves Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves continued heating of the water after the ice has completely melted will now increase the kinetic energy of the liquid molecules and the temperature will rise. For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat. heating and cooling curves are graphs. the energy coming in results in higher potential energy not higher kinetic energy. . Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From www.slideshare.net
Properties of Matter Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves Since temperature is a measure of average kinetic energy, any. Imagine that you have a block of ice that is at a temperature of −30oc − 30 o c, well below its melting point. kinetic energy, potential energy and a heating curve. Breaking up the imf between the molecules leads to a high potential. The ice is in a. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Heating/Cooling Curves & Q= mC Δ T PowerPoint Presentation ID Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves during the horizontal line segments, there is no change in temperature, so kinetic energy remains constant. For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat. Imagine that you have a block of ice that is at a temperature of −30oc − 30 o c, well below its melting point. kinetic energy, potential energy and a heating. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Heating and Cooling Curves PowerPoint Presentation, free download Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves Imagine that you have a block of ice that is at a temperature of −30oc − 30 o c, well below its melting point. Breaking up the imf between the molecules leads to a high potential. the energy coming in results in higher potential energy not higher kinetic energy. heating and cooling curves are graphs. kinetic energy,. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From study.com
Heating & Cooling Curves Definition, Phases & Examples Lesson Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves for example, converting a liquid, in which the molecules are close together, to a gas, in which the molecules are, on average, far apart,. the energy coming in results in higher potential energy not higher kinetic energy. continued heating of the water after the ice has completely melted will now increase the kinetic energy of the liquid. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Heating and Cooling Curves PowerPoint Presentation, free download Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves The ice is in a closed container. the energy coming in results in higher potential energy not higher kinetic energy. Imagine that you have a block of ice that is at a temperature of −30oc − 30 o c, well below its melting point. heating and cooling curves are graphs. Breaking up the imf between the molecules leads. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From www.youtube.com
Heating and Cooling Curves with Calculations YouTube Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves during the horizontal line segments, there is no change in temperature, so kinetic energy remains constant. continued heating of the water after the ice has completely melted will now increase the kinetic energy of the liquid molecules and the temperature will rise. Since temperature is a measure of average kinetic energy, any. Breaking up the imf between the. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Heating and Cooling Curves continued PowerPoint Presentation Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves heating and cooling curves are graphs. for example, converting a liquid, in which the molecules are close together, to a gas, in which the molecules are, on average, far apart,. The ice is in a closed container. during the horizontal line segments, there is no change in temperature, so kinetic energy remains constant. continued heating of. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Heating/Cooling Curves & Q= mC Δ T PowerPoint Presentation ID Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves The ice is in a closed container. heating and cooling curves are graphs. kinetic energy, potential energy and a heating curve. For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat. the energy coming in results in higher potential energy not higher kinetic energy. Since temperature is a measure of average kinetic energy, any. for. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT HEATING AND COOLING CURVES PowerPoint Presentation, free download Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat. Since temperature is a measure of average kinetic energy, any. kinetic energy, potential energy and a heating curve. during the horizontal line segments, there is no change in temperature, so kinetic energy remains constant. for example, converting a liquid, in which the molecules are close together,. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.
From www.excelatphysics.com
Heating Curve ExcelPhysics Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves Imagine that you have a block of ice that is at a temperature of −30oc − 30 o c, well below its melting point. For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat. continued heating of the water after the ice has completely melted will now increase the kinetic energy of the liquid molecules and the temperature. Kinetic And Potential Energy In Heating And Cooling Curves.